
Dynamic Gait Index Test Printable
The Dynamic Gait Index is a clinical test consisting of eight walking tasks, each assigned a score based on the individual's performance. The total DGI score can range from 0 to 24, with higher scores indicating better gait and balance. The tasks and scoring system are as follows:

(PDF) Dynamic gait index Daniela Sadikova Academia.edu
The Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) is a commonly used clinical measure that evaluates the capacity to adapt gait to complex walking tasks commonly encountered in daily life. 1 The DGI is based on a person-environment model of mobility disability (defined as reduced participation in the mobility domain) in which environmental demands are categorized into 8 dimensions—distance, temporal, ambient.

IFA Dynamic Gait Index in Fitness Testing
Introduction The 4-Item Dynamic Gait Index is a shortened version of the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) utilizing only the first four items. It is used for the clinical assessment of walking function and has been examined in patients with balance deficits, vestibular disorders, and those post stroke. [1] [2] Administering Test

Crosswalk 2 Dynamic Gait Index and Haas Balance Book Step workout, Index, Dynamic
Dynamic Gait Index Predicts fall risk in geriatric patients and those suffering from Parkinson's and multiple sclerosis. Key Facts Jump To 1 Gait level surface - walking at normal speed Normal: walks 20', no assistive devices, good speed, no evidence for imbalance, normal gait pattern.

Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) ou Índice Dinâmico da Marcha YouTube
• The Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) was developed to assess the likelihood of falling in older adults by testing eight facets of gait. Link to Instrument Instrument Details Acronym DGI Area of Assessment Balance - Vestibular Balance - Non-vestibular Functional Mobility Gait Assessment Type Observer Administration Mode Paper & Pencil Cost Free CDE Status

Table 2 from Expanding the Scoring System for the Dynamic Gait Index Semantic Scholar
The DGI was developed to examine the ability of patients to maintain functional balance during the performance of activities during gait ( Shumway-Cook et al., 1997 ). The DGI integrates rotational head movements (up and down and from side to side) into gait testing.

Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) YouTube
Similar to 5T-STS is the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI), that verifies the participant's ability to maintain the equilibrium of walking by responding to different requests. Some studies demonstrated the high reliability of the assessment in elderly people, subjects suffering from vestibular dysfunction, multiple sclerosis and post-stroke . It can.

Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) Demonstration UNLV PT '17 YouTube
The aim of the current study is to determine the reliability and validity of the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) for ataxia. Design: Twenty adult participants (23-84 years) with ataxia were evaluated to assess construct validity, inter-rater reliability, and same day test-retest reliability of the DGI. Methods:
PPT Rehabilitation of Balance and Vestibular System Disorders PowerPoint Presentation ID9090436
The Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) assess gait, balance and fall risk in the elderly patients by evaluating usual steady-state walking and walking during more challenging tasks. Intended population are the elderly, stroke patients, and vestibular disorder patients who display poor balance and are at risk for fall. Gait index measures are 8 functional.

Dynamic Gait Index(DGI) Study channel
Human movement can be exceedingly complex to analyze due to highly nonlinear multibody dynamics, nonlinear relationships between muscle excitations and resulting muscle forces, dynamic coupling that allows muscles to accelerate joints and segments they do not span, and redundancy in muscle control [ 1, 2 ].

Dynamic Gait Index Horse Gait
The Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) is one of the tools frequently used to quantify dynamic balance abilities. The purpose of the present study is to better understand its properties and the factors that contribute to this commonly used test in healthy older adults.

Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) & Example Free PDF Download
The purpose of this study was to examine the item fit, redundancy, and unidimensionality of the 8-item Dynamic Gait Index (DGI), 1 which quantifies gait characteristics in people with diagnosed balance and vestibular disorders. Tools to assess balance and gait assist health care professionals in making decisions about intervention and management.

Dynamic Gait Index Horse Gait Nature
The Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) is a gait-related tool developed to identify elderly adults at risk for falls (see Chapter 13 ). It rates the following eight tasks on a 0-3 scale: (1) walking on a level surface, (2) capacity for changing gait speed, (3-4) ability to walk and turn the head in a horizontal and vertical direction, (5) balance for.

Dynamic Gait Index ptpainite
The Dynamic Gait Index evaluates your gait, or how you walk, and your ability to maintain your balance as you walk while performing different tasks. It is most often used to evaluate the risk of falling in older adults. During this test, your therapist will ask you to maintain your balance while you walk and switch from one task to another.

Table 2 from Construction and Validation of the 4Item Dynamic Gait Index Semantic Scholar
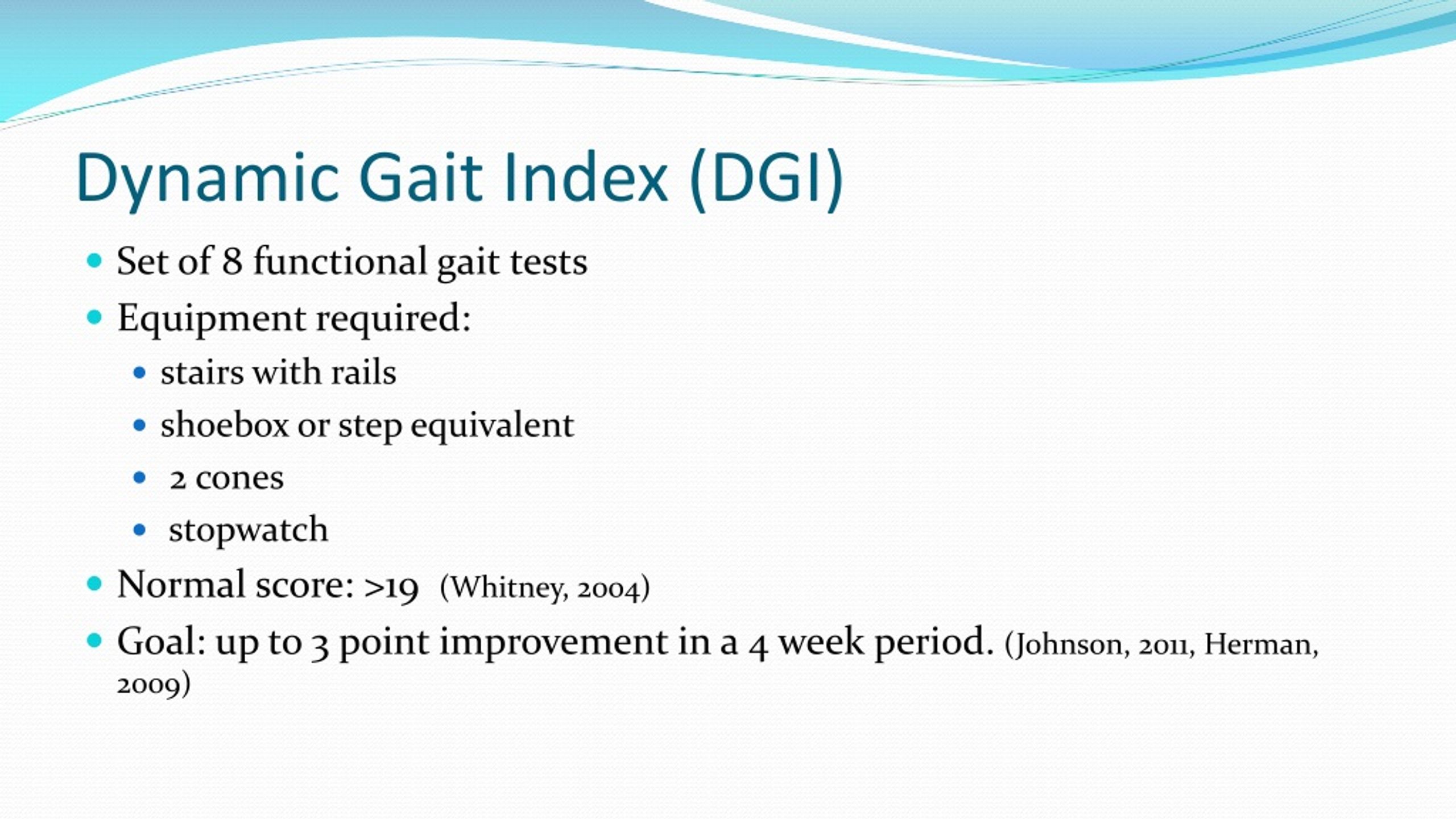
Dynamic Gait Index Description: Developed to assess the likelihood of falling in older adults. Designed to test eight facets of gait. Equipment needed: Box (Shoebox), Cones (2), Stairs, 20' walkway, 15" wide Completion: Time: 15 minutes Scoring: A four-point ordinal scale, ranging from 0-3. "0" indicates the lowest level of

PPT Balance Testing in Older Adults PowerPoint Presentation ID1697572
The Dynamic Gait Index was developed by Anne Shumway-Cook (1995) and has been used with older adults to determine their likelihood of falling. Scores of 19 and less are related to falls in older adults. It tests 8 facets of gait and can be be used with an assistive device. Patient Name: ___________________________________________